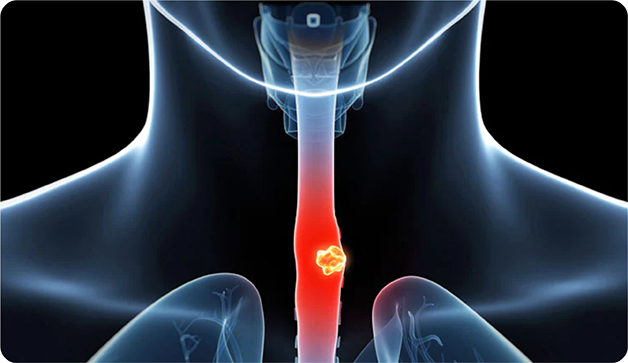
Oesophageal Cancer
The oesophagus or food pipe is a muscular, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. A cancerous growth in the inner lining of this tube leads to oesophagal cancer. The abnormal growth is usually observed in the inner lining, however, in rare cases, it can also occur in the outer layers of the oesophagus. It is one of the major cancers in India due to excessive tobacco and alcohol consumption.

Types of Esophageal Cancer
Depending on its origin, oesophagal cancer is of the following types:
Adenocarcinoma: This type of oesophagal cancer starts from the glandular cells located between the lower oesophagus and upper stomach.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type starts from the squamous cells or the inner lining of the oesophagus.
Small Cell Carcinoma: This rare type starts from the neuroendocrine cells.